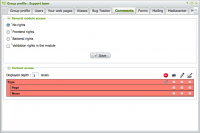
The user management interface allows you to specify the rights for users and user groups.
Example of the modification of rights regarding the content of the "Comments" module:
Assigning rights
Unique user, without associated group(s):
The rights for a user without a group are unique to that user.
User belonging to only one group:
The rights for a user associated with only one group derive from the group.
When a user belongs to one or more groups, their rights derive from their association with this (or these) group(s).
User belonging to one or more groups:
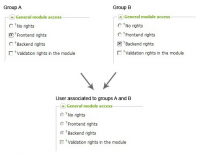
If a user belongs to more than one group, their rights are determined according to the different groups. The user rights are in this way the sum of the rights of the groups to which they belong.
Determining rights:
- Openness takes precedence over closure:
That is to say that if a user is associated with two groups, the rights of the group with greater access will be assigned.
- The more specialized rights take precedence:
For the rights regarding categories or pages, it is always the right concerning the lowest level of the hierarchy which takes precedence.
It is not possible to directly modify the rights of a user belonging to one or more groups: this information appears in grey. In this case you must modify the rights of each of these groups separately.
The fact of not being able to edit the rights of a user belonging to several groups allows you to see clearly the rights derived from their association with these groups: by choosing the user we can thus see, in read-only mode, the rights he has. This can be useful if you want to verify the user's rights after modifying the rights of one of the groups to which they belong.
Example:
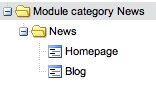
For a "News" module, or the tree of the following categories:
A root category News has 2 children : Homepage and Blog.
Group G1 defines the "See" right in the News category.
Group G2 defines the "Edit" right in the Blog category.
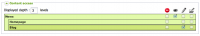
A user associated with group G1 and G2 has the following rights:
Explanations:
For each category Automne calculates the corresponding rights.
- If a right is defined, it retrieves the highest right.
- If no rights are defined, it retrieves the right of the parent category.
That gives us:
- News: "See" (the highest right defined by group G1)
- Welcome: "See" (no definition, thus passed on from the "See" right of the parent category)
- Blog : "Edit" (the highest right defined by group G1)
The different rights to assign
The different pages of this category detail the attribution of rights one can find with the tabs of the user management interface, after having selected a group.


 French
French